POLTEC Technical Data
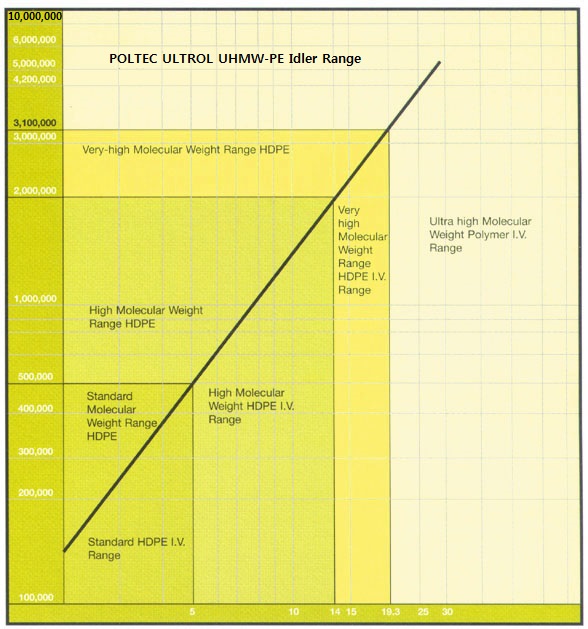
1. 1. POLTEC UHMW-PE Polymer relationship - Intrinsic Viscosity to Molecular Weight
This chart shows the various molecular weights available in polyethylene. Enhanced performance characteristics are directly related to molecular weight. When comparing the abrasion resistance, the higher the molecular weight, the greater the wear life. POTEC UHMW-PE offers exceptional wear resistant properties.
POLTEC is made from the highest molecular weight polyethylene that is consistently available.
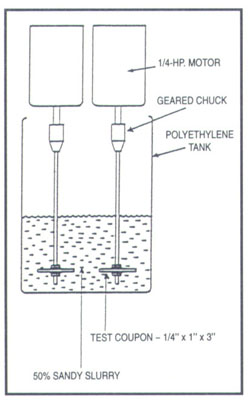
2. 2. Relative Abrasion Resistance - Sand Slurry Test
The abrasion resistance of is POL-TEC clearly demonstrated by measuring its loss of volume against other materials. Test samples are spun for a total of 7.5 hours at 1,750 rpm in a water(50%) and sand(50%) mixture
POLTECUHMW-PE attained an abrasion index rating of 10; results for the other materials tested are shown in relation to POL-TEC. Even though POL-TEC UHMW-PE is exceptionally tough, it is gentle with other materials it works with. UHMW-PE can significantly increase the wear life of contacted moving surfaces. It outwears steel 3 to 1 in sliding wear application.
Material
Abrasion Index
POLTEC UHMW-PE
Nylon 6/6
Polyurethane (D-70)
TFE
HD-PE
Stainless Steel
Polycarbonate
Carbon Steel
Polyacetal
Phosphor Bronze
Phenolic Laminate L.E.
Yellow Brass
Hard Neoprene Rubber
Hickory Wood10
24
27
72
80
84
96
100
110
120
190
400
800
9503. Relative Coefficient of Sliding Friction
This chart compares various materials to UHMW-PE. The lubricating qualities of UHMW-PE eliminate the need for lubrication, significantly reducing downtime and costly maintenance. Its low coefficient of friction allows equipment to operate smoother and quieter. It makes an excellent bearing material reducing friction and drag as well as the amount of wear, noise and abrasion associated with steel parts. UHMW-PE is an local material for dock facing and marine fender.
| Materials Used
|
Relative Coefficient
of Sliding Friction |
| Steel to steel UHMW-PE to Rolled Steel UHMW-PE to Stainless Steel UHMW-PE to UHMW-PE Urethane to Steel Nylon to Steel Teflon to Steel Acetal to Steel |
0.30 - 0.40 0.14 0.13 0.11 0.70 0.20 0.11 0.20 |
4. Physical Properties
This chart shows the physical properties of UHMW-PE. It should be noted that POLTEC UHMW-PE has the highest impact resistance of all thermal plastics. UHMW-PE has an outstanding low temperature impact strength plus high impact energy absorption. As an example of toughness, POLTEC UHMW-PE is used in gears and hammers.
Property
Units
ASTM Procedure
Results
Density at 23℃
Hardness, Rockwell "R"
Ultimate Tensile Strength at 2"/min.
Tensile Yield Strength at 2"/min.
Tensile Yield Elongation at 2"/min.
Elongation at Break at 2"/min.
1% Secant Modulus
Izod Impact at 23℃
Izod Impact at - 40℃
Durometer "D" Hardness
Deflection Temp. at 66 psi
Deflection Temp. at 264 psi
Vicat Softening Point
Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
g/cc
R
psi
psi
%
%
psi
f.p.i.n.
f.p.i.n.
D/15sec
℃
℃
℃D 792
D 785
D 638
D 638
D 638
D 638
D 790B
D 256A
D 256A
D 2240
D 648
D 648
D 1525B
D 696
0.941
64
6400
3400
14
350
175,000
Non-Break
Non-Break
67
80
47
136
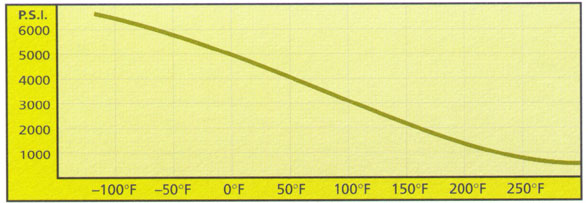
9.1×10-55. Tensile Yield Strength
This chart illustrates the psi of POL-TEC at various temperatures. At 72oF, UHMW-PE exhibits exceptional tensile strength on which a weight basis is better than that of steel.
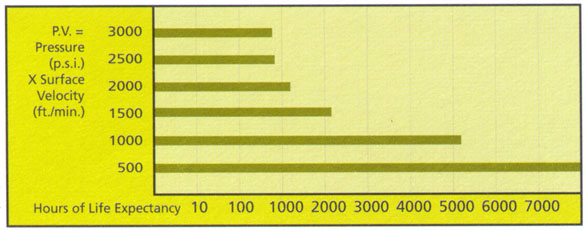
6. Compression Deformation
This chart illustrates the compression strength of POLTEC UHMW-PE for engineering purposes.
7 .UHMW-PE Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
This chart illustrates the chemical resistance of POLTEC UHMW-PE. Strong oxidizing agents and most aggressive chemicals have virtually no effect. UHMW-PE does not absorb moisture, bacteria, fungus growth and ice will not adhere to its surface, POL-TEC is an ideal material for parts operating in a chemical and corrosive environment such as sewage treatment and chemical processing plants.
|
Inorganic |
At 22.2 ℃ |
At 60 ℃ |
|||||
|
Chemical |
Time(days) |
Weight ch- ange (%) |
Appearance |
Time(days) |
Weight ch-ange (%) |
Appearance |
|
|
Chromic Acid (1N) |
30 |
+ 0.34 |
Slight Yellow |
10 |
- 0.15 |
Slight yellow |
|
|
Hydrochloric Acid,37% |
30 |
+ 0.24 |
Light Tan |
10 |
+ 0.40 |
Tan |
|
|
Hydrogen Peroxide, 30% |
30 |
- 0.01 |
No change |
10 |
+ 0.04 |
No change |
|
|
Nitric Acid, 50% |
30 |
+ 0.78 |
Brittle, attacked |
10 |
+ 4.44 |
Brittle, attacked |
|
|
Phosphoric Acid, 85% |
30 |
+ 0.07 |
No change |
10 |
+ 0.03 |
No change |
|
|
Sodium Hydroxide, 30% |
5 |
- 0.50 |
No change |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
Sodium Hypochlorite |
30 |
+ 0.04 |
No change |
10 |
+ 0.21 |
No change |
|
|
Sulfuric Acid, Fuming |
- |
- |
Decomposed in 1 Day |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
100% |
30 |
+ 0.26 |
Slight change |
10 |
+ 1.00 |
Black, attacked |
|
|
50% |
30 |
- 0.06 |
No change |
10 |
- 1.14 |
Slight change |
|
|
Water, Synthetic Sea |
30 |
+ 0.13 |
No change |
10 |
+ 0.22 |
No change |
|
|
Organic |
Acetic Acid |
30 |
+ 0.87 |
Slight Brown |
8 |
+ 0.83 |
Slight brown |
|
Acetone |
30 |
+ 0.24 |
No change |
4 |
+ 0.45 |
No change |
|
|
Benzene |
30 |
+ 6.30 |
Slight change |
4 |
+ 8.11 |
Slight change |
|
|
Carbon Tetrachloride |
30 |
+ 18.8 |
Swelled, attacked |
4 |
+ 22.4 |
Swelled, attacked |
|
|
Ethanol |
30 |
+ 0.03 |
No change |
4 |
- 0.01 |
Slight change |
|
|
Ethyl Acetate |
30 |
+ 1.34 |
Slight change |
4 |
+ 1.86 |
Slight change |
|
|
Ethyl Ether |
30 |
+ 3.9 |
Slight change |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
Ethylene Dichloride |
30 |
+ 12.2 |
Swelled, attacked |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
Gasoline |
30 |
+ 4.81 |
Slight change |
4 |
+ 6.61 |
Slight change |
|
|
Oil, Licensed |
30 |
- 0.70 |
No change |
8 |
- 0.23 |
No change |
|
|
Olive |
30 |
- 0.50 |
No change |
8 |
- 0.12 |
No change |
|
|
Transformer |
30 |
+ 2.4 |
Slight change |
8 |
+ 6.35 |
Slight swelling |
|
|
Toluene |
30 |
+ 7.0 |
Slight swelling |
8 |
+ 10.9 |
Slight swelling |
|
|
Trichlorethylene |
30 |
+ 15.0 |
Swelling, brown |
8 |
+ 26.3 |
Swelled |
|
|
Xylene |
30 |
+ 7.1 |
Slight swelling |
8 |
+ 15.5 |
Swelled |
|